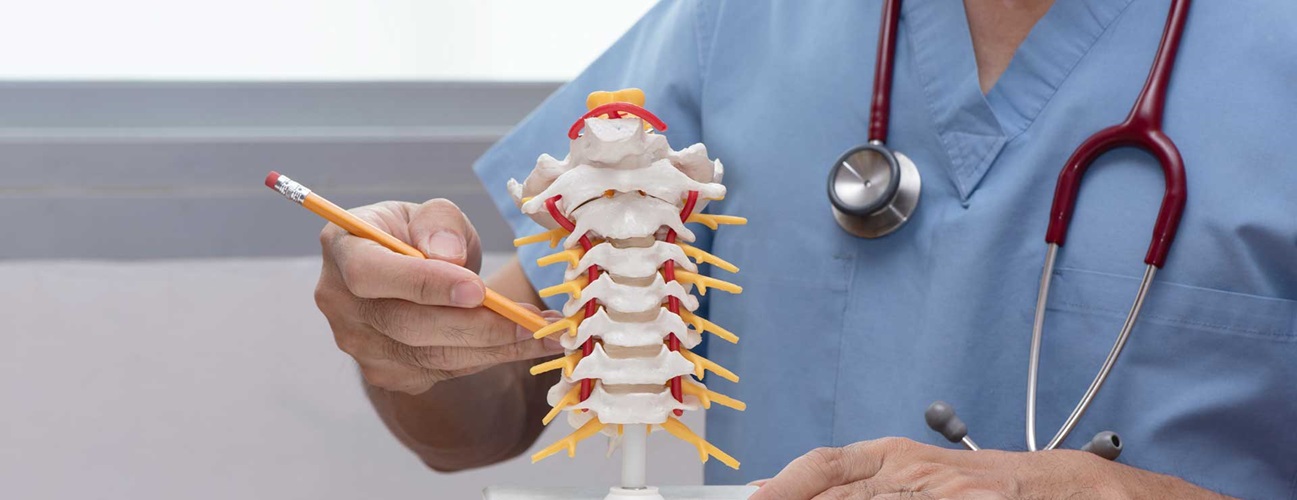
Spinal instability occurs when the spine loses its normal alignment or function, leading to chronic back pain, numbness, and difficulty with movement. Dr. Larry Davidson, a recognized expert in spinal surgery, has seen that this condition can potentially result from various causes, including degenerative disc disease, trauma, spinal deformities, or previous surgeries. When non-surgical treatments fail to provide sufficient relief, spinal fusion is often recommended to stabilize the spine and prevent further deterioration. Advances in surgical techniques and technologies have made spinal fusion more precise, less invasive, and increasingly successful.
Understanding Spinal Instability
Spinal instability refers to the spine’s inability to maintain its normal alignment under physical stress, leading to abnormal movement between vertebrae. This can result in pain, nerve compression, and other neurological symptoms. Conditions such as spondylolisthesis, where one vertebra slips over another, and degenerative disc disease, which weakens the spinal discs, are common causes of instability. Trauma, such as fractures or injuries, can also destabilize the spine, causing misalignment and compromised function.
For patients with severe spinal instability, spinal fusion offers a solution by fusing two or more vertebrae to prevent abnormal movement and restore stability. By eliminating motion between the affected vertebrae, the procedure can alleviate pain, improve mobility, and prevent further damage to the spine.
How Spinal Fusion Stabilizes the Spine
Spinal fusion surgery involves permanently joining two or more vertebrae to create a single, solid bone structure. This is typically achieved by placing bone grafts between the affected vertebrae. Over time, the bone grafts grow and fuse the vertebrae, eliminating any abnormal movement between them. The procedure also involves the placement of hardware, such as screws, rods, or plates, to provide immediate stability and support while the fusion process occurs.
The primary goal of spinal fusion is to stop abnormal movement in the spine, which can help reduce pain and improve function. For example, in cases of spondylolisthesis, where a vertebra has slipped out of place, spinal fusion helps realign the spine and prevent further slippage. Similarly, for patients with degenerative disc disease, spinal fusion eliminates the painful motion between vertebrae, restoring stability to the spine.
Best Practices for Spinal Fusion Surgery
To achieve the best outcomes from spinal fusion surgery, surgeons follow several essential best practices to ensure the procedure’s success and minimize risks:
- Preoperative Planning: A detailed evaluation of the patient’s condition is crucial. Surgeons utilize advanced imaging techniques, such as CT scans and MRIs, to assess the extent of spinal instability and plan the precise placement of bone grafts and hardware. This plan also includes selecting the most suitable bone graft material based on the patient’s health and surgical requirements.
- Bone Grafting Options: While autografts—bone harvested from the patient’s pelvis—have traditionally been the standard, advancements now offer alternatives like allografts (donor bone) and synthetic bone grafts. These substitutes eliminate the need for a second surgical site, reducing pain and speeding up recovery.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Minimally invasive spinal fusion techniques have become popular for reducing surgical trauma. Using smaller incisions and specialized instruments, surgeons can access the spine with less muscle damage, reduced blood loss, and shorter hospital stays, offering patients a faster, less painful recovery.
- Postoperative Care: Effective recovery requires proper postoperative care. Physical therapy is critical for rebuilding strength and flexibility, while pain management—through medications and non-pharmacological methods like ice therapy—helps ensure comfort during recovery. Patients must also avoid activities that could strain the healing spine to prevent complications.
Innovations Enhancing Spinal Fusion Procedures
Recent innovations in spinal fusion surgery have significantly improved the precision, safety, and outcomes of the procedure. These advancements are making spinal fusion a more effective solution for patients with spinal instability:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems like Mazor X and ExcelsiusGPS have revolutionized spinal fusion by providing surgeons with greater precision during the procedure. These systems use preoperative imaging to create a 3D map of the patient’s spine, which helps guide the surgeon’s movements with millimeter accuracy. Robotic-assisted surgery reduces the risk of human error, ensures precise placement of screws and hardware, and minimizes tissue damage, resulting in faster recovery times and improved outcomes.
- 3D-Printed Implants: 3D printing technology has made it possible to create customized spinal implants tailored to the patient’s unique anatomy. These implants provide a more precise fit than traditional, off-the-shelf implants, improving stability and promoting better bone fusion. 3D-printed implants can be designed with porous structures that encourage bone growth through and around the implant, enhancing the fusion process and reducing the risk of implant failure.
- Bone Growth Stimulators: Bone growth stimulators are devices that use electrical or ultrasonic energy to stimulate bone growth at the fusion site. These devices are typically worn externally over the surgical area and are used daily during the initial stages of recovery. Bone growth stimulators can accelerate the fusion process and improve outcomes, particularly for patients with risk factors such as osteoporosis or a history of smoking, which can slow bone healing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Surgical Planning: AI technology is being integrated into spinal fusion surgeries to enhance preoperative planning and intraoperative decision-making. By analyzing data from previous surgeries and patient outcomes, AI can help surgeons predict the most effective surgical techniques and improve the accuracy of hardware placement. AI systems also provide real-time feedback during surgery, alerting the surgeon to any potential issues and helping to optimize the procedure’s success.
Spinal fusion surgery remains one of the most effective treatments for stabilizing the spine in cases of spinal instability. With the introduction of minimally invasive techniques, robotic assistance, 3D-printed implants, and bone growth stimulators, the procedure has become more precise, less invasive, and more successful than ever before. These innovations not only enhance the safety and accuracy of the surgery but also lead to faster recovery times and improved long-term outcomes for patients.
As technology continues to advance, spinal fusion surgery is poised to become even more effective, offering patients more options for achieving spinal stability and long-term pain relief. Dr. Larry Davidson highlights that by integrating best practices with cutting-edge technologies, surgeons can help deliver the highest level of care to patients with spinal instability. These advancements can help patients regain mobility and potentially improve their overall quality of life.